In a usual wing the elevating force is created only with 2/3 surfaces as other 1/3 is engaged in division of a stream of air.
As against prototypes all area of the submitted wing creates elevating force.
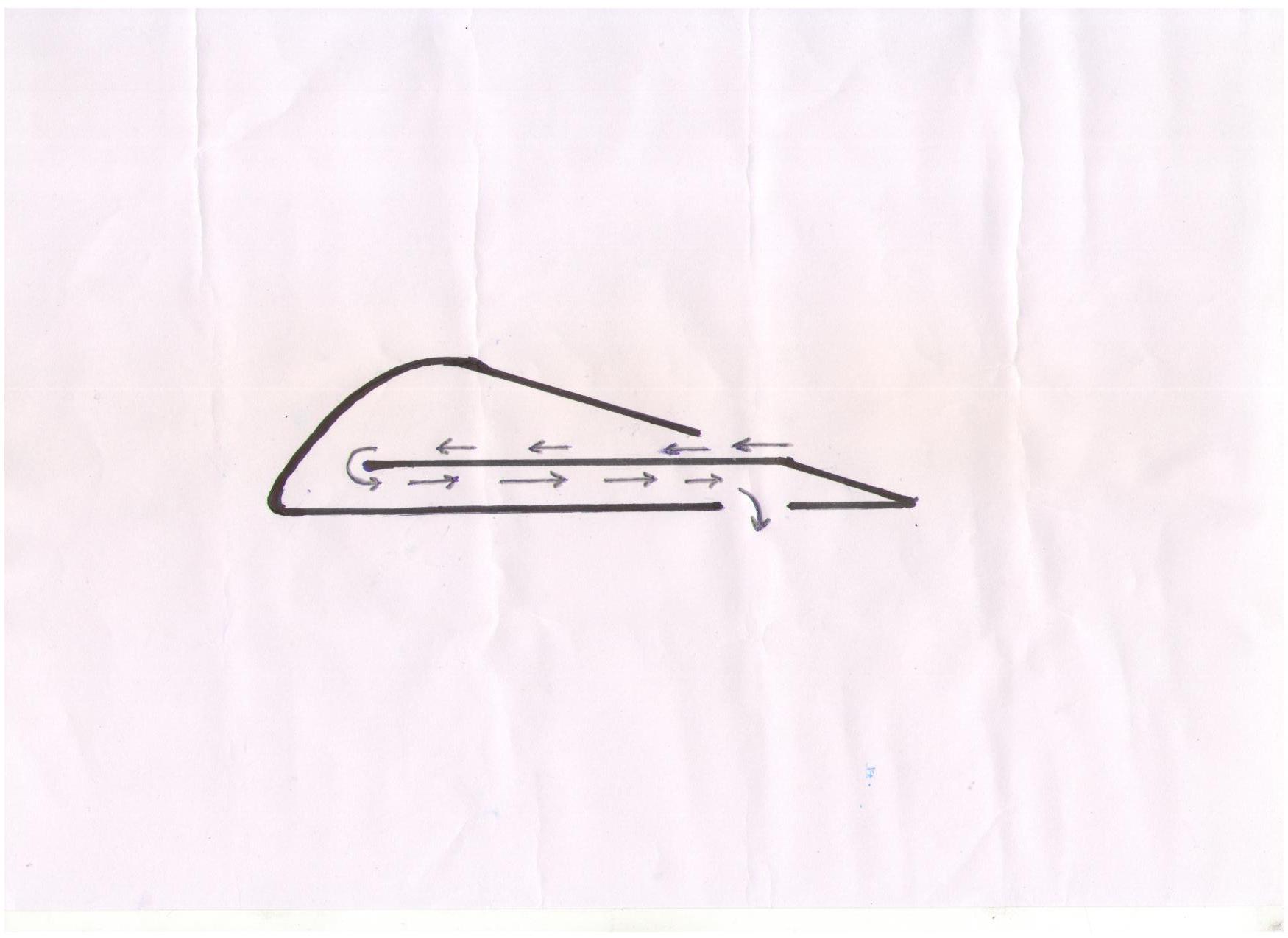
This effect is reached by that on the top surface of a wing in a zone of the lowest pressure there is a cut. This cut opens a cavity inside a wing. The wing should be hollow (i.e. to have free space between longerons and other devices) and closed from lateral faces.
During flight under the Pasсals law inside a wing the same low pressure is created which is at a back edge of a wing . Thus there is a difference of pressure around of the bottom covering of a wing. The area of this covering is on 30 % more, than the area of that top surface above which the difference of pressure is created.
Thus elevating force of this wing is a minimum on 30 % more than at usual.
During supersonic flight inside a wing the vacuum is created as air has not time to come inside a wing. Elevating force means will be more. It is possible to do such cuts on propellers too.
With the purpose of reduction of turbulence, the quantity of cuts can be more. For example the second cut can be made on the top part of a wing, at once behind that "camber" which divides a stream of air. In this case the effect will not vanish. On the contrary - it can be will increase - as pressure above a wing and inside a wing will be balanced and become equally low.
This principle will be more effective on a wind and water-wheels. Cuts on blades increase the area of pressure of a wind or water a minimum by 50 %. Hence capacity increases too. Cavitation on water-wheels will decrease. Pressure inside the blade will not be compensated by pressure from above. On the contrary - they will be summarized.
http://www.createthefuturecontest.com/2014/entries/sustainable-technologies/4344
|